
Table of Contents
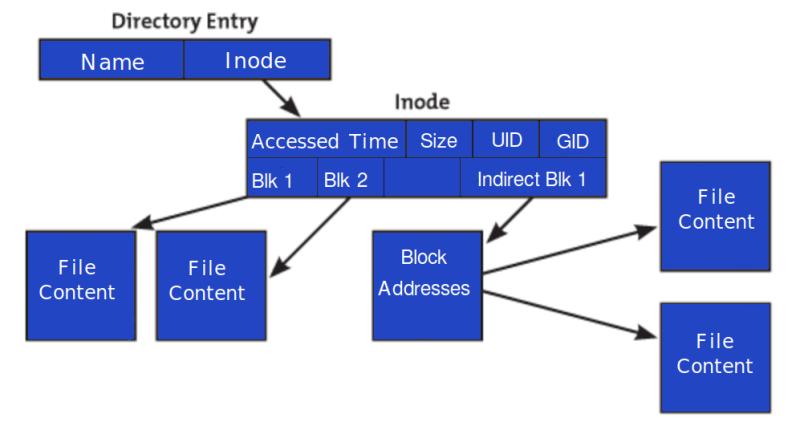
Inode is a data structure that keeps the information about a file on your hosting account. The number of inodes indicates the number of files and folders you have. This includes everything on your account, emails, files, folders, and anything you store on the server.
Inodes are essential for the file system to manage and organize files and directories efficiently. They allow the operating system to track and access files quickly, as well as perform operations such as file allocation, file deletion, and file metadata retrieval.
Inode features:
- File System Structure: Web hosting servers typically use file systems that employ inodes to manage files and directories. Each file and directory on the server is associated with an inode, which stores metadata such as file attributes, ownership, and pointers to data blocks.
- Resource Allocation: Hosting providers often impose limits on inode usage as part of their hosting plans. These limits are separate from disk space and bandwidth quotas and are intended to prevent abuse and ensure fair resource allocation among hosting accounts.
- Inode Consumption: Inodes usage increases with the creation of files, directories, emails, and other resources within the hosting account. Every file, directory, email, and other object consumes one or more inodes, depending on the file system’s configuration and parameters.
- Impacts of Exceeding Limits: Exceeding the allocated inode limit can result in various issues, including performance degradation, resource contention, and suspension of the hosting account. Hosting providers may enforce inode limits to prevent excessive usage that could negatively impact server stability and performance.
- Managing Inode Usage: To avoid exceeding inode limits, hosting account owners can take several measures, such as:
- Regularly deleting unnecessary files and directories.
- Optimizing website code and file structures to reduce the number of files and inodes used.
- Archiving or compressing old files to reduce inodes consumption.
- Avoiding excessive email storage and attachments.
- Monitoring inode usage through hosting control panels or command-line tools and taking corrective actions as needed.
Attributes of an Inode and How it Works:
Inodes are found at the start of a partition. This partition acts as a boundary in your web hosting account disk that indicates how much space a file system can use.
When you create a new file, the system assigns a file and inode number, which it stores as entries in an index. If you search for a file by name, the system looks for the associated inode number in the file directory where it resides.
- Owner
- Size
- File User ID
- File Group ID
- Device ID
- File creation date
- Permissions and Access control
- File types
- Number of hard links
- Metadata information.
The number of inodes on your web hosting account shows how many files, directories, emails, or other items you have on your account.
How to Check Inode Usage in control Panel:
1.Log into your control panel User Interface.
2.On the right corner, under Resources, you’ll see the disk and inode usage, among other stats.

To see detailed statistics of disk usage for all files and folders on your account, navigate to Files and click on Disk usage. Select any folder to view its content.
You can control individual accounts’ disk space and inode quotas from control Panel’s Admin Interface.
How to Free Up the Number of Inodes Your Account Uses:
Since the inode usage on your account affects the number of files and folders you can create, you must reduce your inode count by reducing files and folders you don’t need.
You can do this through the File Manager or accessing your files to an FTP client—Filezilla.
Delete and Uninstall Inactive Plugins:
If you use WordPress, please uninstall any plugins that aren’t in use on your blog. When you deactivate the plugins, the codebase remains on your account and consumes your inodes limit.
Delete Unnecessary Backup Files:
Sometimes, scheduled plugins or third-party services can fill up your disk space if left unchecked. To save disk space and inodes, download and delete unused backups from your account.
Clear Your Cache Regularly:
It’s usual for many web applications these days to use file caching. This can take up disk space on your account, thus affecting the total inode limit.
To check this, reduce cached files stored in the website’s cache folder.
Reduce Unnecessary Emails:
Clear out your trash and spam folders regularly, as they can store up many unnecessary emails.
While you’re at it, now is the best time to deactivate emails from newsletters you never read.
Conclusion:
In summary, inode usage in hosting refers to the consumption of inodes by files, directories, emails, and other resources within a hosting account. Hosting providers may impose inode limits to ensure fair resource allocation and prevent abuse, and customers are responsible for managing their inode usage to avoid exceeding these limits.